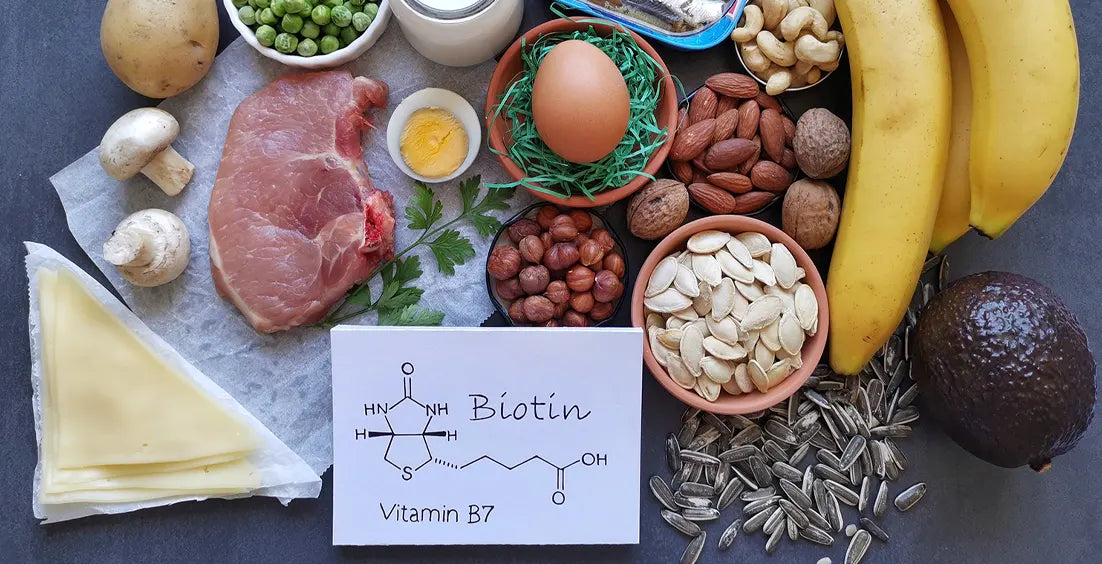
How Does Biotin Improve Skin and Hair?
Biotin, also known as the wonder vitamin, promotes well-being and health. B-vitamins are essential for converting food into energy, supporting metabolism, and maintaining hair, skin, and nails.
Advertiser Disclosure: WOWMD independently vets all recommended products. If you purchase a featured product, we may be compensated. Learn why you can trust us.
Popular Stories
- Best Foods for ED: Top Diet Tips for Better Sexual Health
- Best Supplements for Erectile Dysfunction: Boost Performance & Vitality
- Top Supplements to Lower Cortisol, Manage Stress & Boost Energy in 2025
- Best Prostate Supplements: Top Picks for 2025
- Best Beetroot Supplements in 2025: Top 5 Picks
- 6 Best Face Serums For ALL Skin Problems
References
WOWMD follows strict sourcing guidelines to ensure the accuracy of its content, outlined in our editorial policy. We use only trustworthy sources, including peer-reviewed studies, qualified experts, and information from top institutions.
- Biotin - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554493/#:~:text=%5B8%5D%20Biotin's%20mechanism%20of%20action,is%20a%20carrier%2Dmediated%20process.
- Evaluation of biophysical skin parameters and hair changes in patients with acne vulgaris treated with isotretinoin, and the effect of biotin use on these parameters - PubMed (nih.gov) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33682085/#:~:text=Conclusion%3A%20Biotin%20(10%20mg%2F,adverse%20effects%20of%20isotretinoin%20treatment.
- Biotin Deficiency - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547751/#:~:text=Dermal%20abnormalities%20in%20biotin%20deficiency,to%20that%20of%20zinc%20deficiency.
- A Review of the Use of Biotin for Hair Loss - PMC (nih.gov) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5582478/
- A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study Evaluating the Efficacy of an Oral Supplement in Women with Self-perceived Thinning Hair - PMC (nih.gov) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3509882/
- Biotin - Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline - NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114297/
- Biotin for the treatment of nail disease: what is the evidence? (pubmed) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29057689/


 Alpha Man Power Pack
Alpha Man Power Pack All-Day Fat Burn Trio
All-Day Fat Burn Trio Better Immunity Bundle
Better Immunity Bundle  Calm & Sleep Duo
Calm & Sleep Duo Cognitive Health & Vision Combo
Cognitive Health & Vision Combo Complete Weight Loss Bundle
Complete Weight Loss Bundle Core Vitality Trio
Core Vitality Trio Energy Booster Combo
Energy Booster Combo Focus Fuel Trio
Focus Fuel Trio Glow & Balance Duo
Glow & Balance Duo Health Balance Trio
Health Balance Trio Heart Care Bundle
Heart Care Bundle Joint Health Support Combo
Joint Health Support Combo Men's Immunity & Prostate Health Bundle
Men's Immunity & Prostate Health Bundle Metabolism Boost Duo
Metabolism Boost Duo Natural Skin Care Bundle
Natural Skin Care Bundle Peak Performance Duo
Peak Performance Duo Relax & Recharge Duo
Relax & Recharge Duo Skin Detoxification Bundle
Skin Detoxification Bundle Smart Energy Trio
Smart Energy Trio Stress + Energy + Wellness Combo
Stress + Energy + Wellness Combo  Total Burn Ignite Trio
Total Burn Ignite Trio Total Harmony Pack
Total Harmony Pack Workout Supplements Combo
Workout Supplements Combo