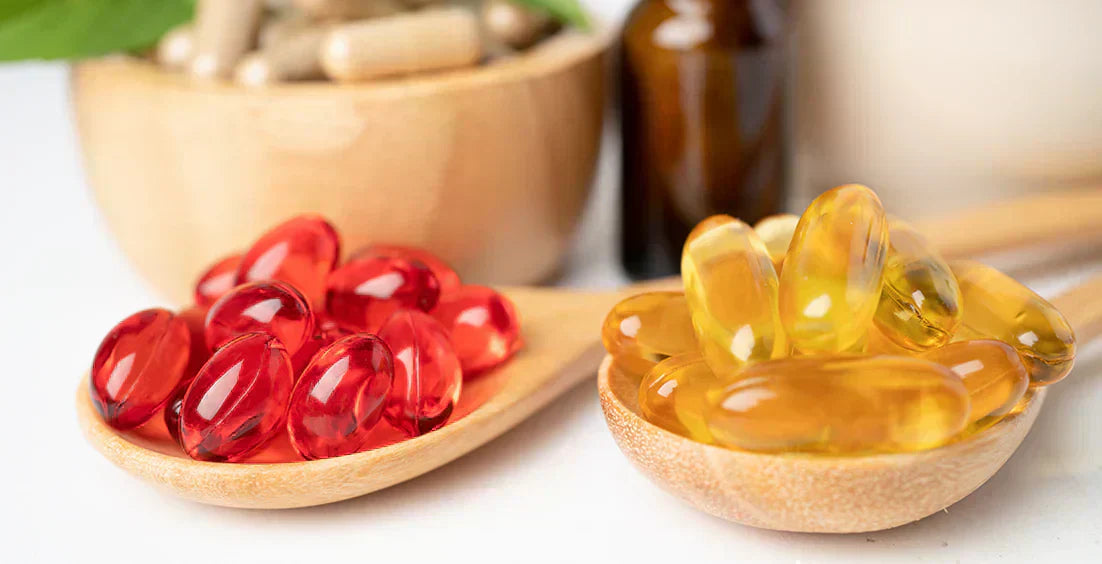
Is Krill Oil Better Than Fish Oil?
Krill oil and fish oil are popular dietary supplements that provide omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to support health benefits. Learn more about the differences between krill oil & fish oil and find out which is better for you.
Advertiser Disclosure: WOWMD independently vets all recommended products. If you purchase a featured product, we may be compensated. Learn why you can trust us.
You May Also Like
Popular Stories
- The Best Beef Tallow Products for Radiant Skin: A 2026 Guide
- Holy Basil : Ayurveda’s Herb for Balance, Immunity & Everyday Calm
- Best Gel Moisturizers for Hydration & Skin Care in 2026
- 7 Best Effective Supplements for Improving Bladder and Prostate Health in 2026
- 4 Best Cooling Gels for Skin and Body: Instant Refreshment and Relief
- 4 Best Hyaluronic Acid Serums for Skin Hydration - Tested & Reviewed
References
WOWMD follows strict sourcing guidelines to ensure the accuracy of its content, outlined in our editorial policy. We use only trustworthy sources, including peer-reviewed studies, qualified experts, and information from top institutions.
- Impact of Antarctic Krill Oil Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Injury Recovery After Resistance Exercise: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36566465/
- The Effects of Fish Oil on Cardiovascular Diseases: Systematical Evaluation and Recent Advance: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8767101/
- Associations of Fish Oil Supplementation with Incident Dementia: Evidence From the UK Biobank Cohort Study: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2022.910977/full
- Comparison of Bioavailability of Krill Oil Versus Fish Oil and Health Effect: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4559234/
- Lipid-Modifying Effects of Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil: A Network Meta-Analysis: https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article-abstract/78/9/699/5740623
- Evaluation of the Effects of Neptune Krill Oil on the Clinical Course of Hyperlipidemia: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15656713/
 Alpha Man Power Pack
Alpha Man Power Pack All-Day Fat Burn Trio
All-Day Fat Burn Trio Better Immunity Bundle
Better Immunity Bundle  Calm & Sleep Duo
Calm & Sleep Duo Cognitive Health & Vision Combo
Cognitive Health & Vision Combo Complete Weight Loss Bundle
Complete Weight Loss Bundle Core Vitality Trio
Core Vitality Trio Energy Booster Combo
Energy Booster Combo Focus Fuel Trio
Focus Fuel Trio Glow & Balance Duo
Glow & Balance Duo Health Balance Trio
Health Balance Trio Heart Care Bundle
Heart Care Bundle Joint Health Support Combo
Joint Health Support Combo Men's Immunity & Prostate Health Bundle
Men's Immunity & Prostate Health Bundle Metabolism Boost Duo
Metabolism Boost Duo Natural Skin Care Bundle
Natural Skin Care Bundle Peak Performance Duo
Peak Performance Duo Relax & Recharge Duo
Relax & Recharge Duo Skin Detoxification Bundle
Skin Detoxification Bundle Smart Energy Trio
Smart Energy Trio Stress + Energy + Wellness Combo
Stress + Energy + Wellness Combo  Total Burn Ignite Trio
Total Burn Ignite Trio Total Harmony Pack
Total Harmony Pack Workout Supplements Combo
Workout Supplements Combo